9. Elevation Data#
This page is a Jupyter Notebook that can be found and downloaded at the GitHub repository.
import rioxarray as rxr
import pdemtools as pdt
import geopandas as gpd
import pystac_client
import planetary_computer
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from shapely.geometry import box
9.1. Global elevation datasets#
Microsoft Planetary Computer has a large range of DEMs available. We can download them using pystac_client.
catalog = pystac_client.Client.open(
"https://planetarycomputer.microsoft.com/api/stac/v1",
modifier=planetary_computer.sign_inplace,
)
arolla_bounds = [7.483, 45.954, 7.545, 45.990]
arolla_gdf = gpd.GeoDataFrame(geometry=[box(*arolla_bounds)], crs=4326)
search = catalog.search(
collections=["cop-dem-glo-90"],
bbox=arolla_bounds,
)
items = list(search.items())
print(f"Returned {len(items)} items")
Returned 1 items
copdem = rxr.open_rasterio(items[0].assets['data'].href).rio.clip(arolla_gdf.geometry.values).squeeze()
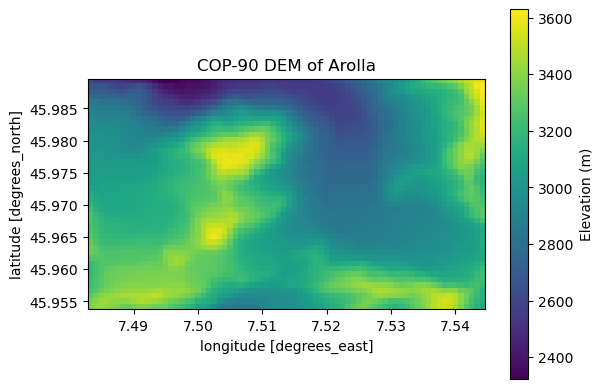
OK, let’s plot:
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
copdem.plot.imshow(ax=ax, cbar_kwargs={'label': 'Elevation (m)'})
ax.set_aspect('equal')
ax.set_title('COP-90 DEM of Arolla')
plt.show()
9.2. ArcticDEM and REMA: pdemtools#
The above is fine for downloading large-scale global DEMs. For managing ArcticDEM and REMA DEMs and strips, I have written an entire Python package called pdemtools for downloading, coregistering, calculating hillshades and terrain attributes, etc. I will not add any more documentation here as you can consult the pdemtools website!
9.3. Calculating Crevasse Depths#
If you’re reading this, it might be likely that you’re working with me to calculate crevasse depths. The crevdem tool is available at this GitHub repo, and documentation is contained therein.
